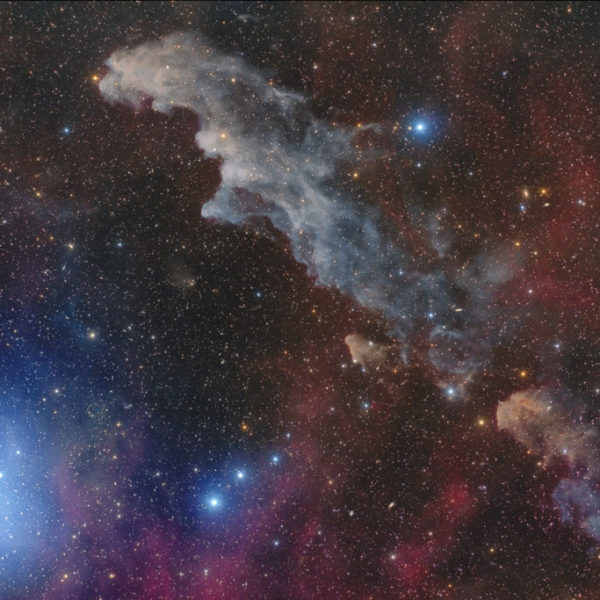
Nebulae are clouds of gas and dust, many of which can be found in our galaxy or other galaxies. Because nebulae play a role in the birth and death of stars, these regions play an important role for astronomers looking to understand how stars form and die. Some black holes are the result of star death. These large clouds of dust are interesting targets for observers not only for astronomers but also for amateur observers. Nebulae are not as bright as stars or planets, but they are incredibly beautiful and are often the subject of interest to photographers. Some of the most complex and accurate images of these areas come from telescopes such as the Hubble Space Telescope.
What is the formation of nebula like?
According to astronomy science, a nebula forms when parts of the interstellar environment undergo gravitational collapse. Mutual gravitational attraction causes matter to coalesce to form more and more dense regions. Hence, stars form at the center of decaying material, where ionizing ultraviolet light makes the surrounding gases visible at light wavelengths.
Most nebulae are large, reaching hundreds of light-years in diameter. Although nebulae are denser than the space around them, most nebulae are less dense than any vacuum created in the earthen environment. A nebula cloud that is similar in size to Earth is about the size of the matter, weighing only a few kilograms.
Types of nebulae
How is the nebula classified?
Stellar objects, which can be called nebulae, exist in four main groups:
- diffuse nebula
- dark nebula
- planetary nebula
- Supernova Remnant Nebulae
1. Diffuse Nebula
Most of them fall into the category of diffuse nebulae, meaning that they have no definite boundaries.
How are diffuse nebulae formed?
An emission nebula is a cloud of matter in which very bright and burning stars are located. The light of these stars in the ultraviolet spectrum excites hydrogen and oxygen atoms, resulting in a relatively large amount of light emitted from the nebula.
In other words, in these nebulae, atoms are ionized by ultraviolet radiation from hot stars, followed by re-radiation, but this time in the visible light spectrum. Diffuse nebulae themselves fall into two categories: Luminous nebulae( Reflection nebulae and emission nebulae) and dark nebulae.
1.1. Luminous nebula
Reflection nebula
In contrast, reflective nebulae do not emit a significant amount of visible light, but they are still bright because they reflect the light of nearby stars. It is when gaseous gases and particles are placed in the vicinity of a hot, bright star, and significant light is produced by the excitation of atoms.
Emission nebula
Emission nebulae are those that emit radiation from the spectral line of ionized gases and are often called HII regions because they are composed of ionized hydrogen. Occurs when stars die, the hot remnants of the star emit radiation. In this case, we can refer to supernova remnant nebulae and planetary nebulae.
2. Supernova Remnant Nebula (emission)
This type of nebulas forms as a result of explosions and is therefore classified as supernova remnant nebulae.
How does the Supernova Remnant nebula form?
In this case, short-lived stars explode in their nuclei, exploding their outer layers. The blast leaves debris in the form of a compact body, a neutron star, and a cloud of gas and dust ionized by the blast energy.
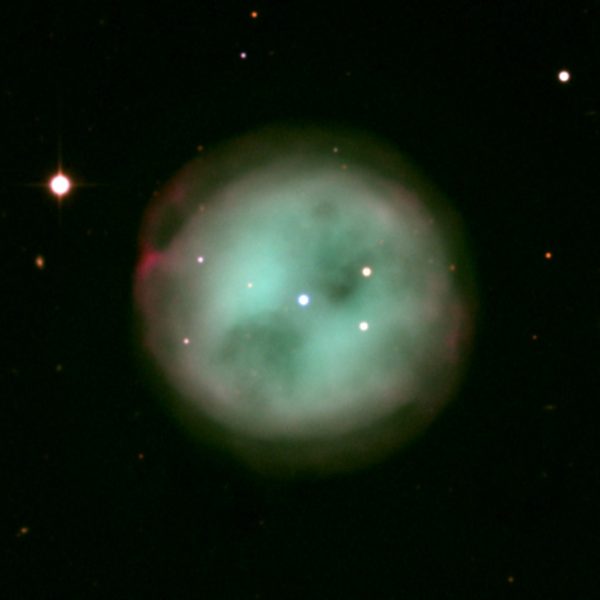
3. Planetary Nebula(emission)
It is a type of emission nebula composed of plasma and gas. The reason for this naming, which originated in the eighteenth century, is that due to the circularity of these nebulae (which is due to the explosion of stars) in weak telescopes, it has been seen as a planet and has been confused with the planet. The lifespan of these nebulae is short, about a few tens of thousands of years, compared to the star’s millions of years.
How does a planetary nebula form?
The formation of a planetary nebula involves the entry of a low-mass star into the last stage of life. In this scenario, the stars enter the phase of their red giant and slowly lose their outer layers due to the blinking of helium inside them. When a star loses enough material, its temperature rises and the ultraviolet light emitted ionizes the surrounding material it has thrown.
4. Dark Nebula
Astronomers believe that stars are born inside these nebulae. Dark nebulae may have masses several thousand times greater than those of the Sun.
How do dark nebulae form?
Dark nebulae, also known as absorption nebulae, are composed of dust and gas, and because of this dust, they strongly absorb light and are dark. If a nebula has enough mass, at some point in time its material will compress and become a star. But if dark nebulae have low mass or high temperature, they will scatter in space and disappear!
How are nebulae detected?
Most nebulae can be best detected using telescopes. Some nebulae, such as the Hunter Nebula, are difficult to see with the naked eye. Using telescope magnifications, it will be much easier to see nebulae because magnification allows the viewer to see more light from the object. Planetary nebulae are classified as the faintest nebulae, which are shorter in age than other nebulae. Astronomers believe that these nebulae will disappear only ten thousand years after their formation. But H2 regions last as long as they have enough material to continue star formation. These areas are easier to see because of the radiance of the stars that make them glow.
Conclusion
In short, when a star reaches the end of its life, it begins to pulsate and slowly eject its layers of gas, these layers are hot and therefore will begin to radiate the emission spectrum.
These layers expand so wide that they create beautiful objects called planetary nebulae. But because these layers are low mass and hot, and have an initial velocity toward their eccentricity, it can be fairly well assumed that there is no chance of gravitational shrinkage again and that in the very distant future these nebulae will be fully propagated in space. They will be and no trace of them will remain and their central star will also cool down and turn into a white dwarf.
And finally, if the stars are heavy (much larger than the mass of the Sun), when they reach the end of their life, their life ends with a supernova explosion, and a significant part of the star’s mass is ejected in this explosion and a huge amount of energy in the form of light. Is sent. The nebula created from the remnants of these stars is called the supernova remnant nebula.






Contact me

